Understanding Sugar Withdrawal Symptoms: A Complete Guide

Taming the Sugar Beast: Understanding Withdrawal
Quitting sugar? Prepare for sugar withdrawal symptoms. This listicle outlines six common symptoms, providing knowledge to conquer your cravings and reclaim your health. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for managing expectations and staying committed to a sugar-free lifestyle. We'll cover intense sugar cravings, fatigue and energy crashes, mood swings and irritability, headaches, sleep disturbances, and difficulty concentrating. This information empowers you to navigate the challenges and achieve long-term freedom from sugar.
1. Intense Sugar Cravings
One of the most significant hurdles you'll face when reducing your sugar intake is the onset of intense sugar cravings. This is the most common and immediate sugar withdrawal symptom, characterized by powerful urges to consume sweet foods. These cravings aren't simply a lack of willpower; they have a physiological basis. Your brain has become accustomed to the dopamine releases triggered by sugar consumption. When you reduce your sugar intake, your brain essentially panics, signaling for more to maintain what it perceives as its 'normal' state. Understanding this mechanism is crucial for successfully navigating sugar withdrawal and achieving long-term dietary changes. This is why managing these cravings effectively deserves its place as the number one item on this list of sugar withdrawal symptoms.
These cravings are a hallmark of sugar withdrawal and a sign that your body is beginning its detoxification process. They typically peak in intensity within the first 2-3 days after reducing sugar intake and can last for 1-2 weeks, sometimes longer. These cravings aren't constant but often appear in waves, triggered by factors like stress, fatigue, or even specific times of day, such as after meals or during afternoon energy dips. You might experience obsessive thoughts about food, find yourself constantly thinking about sugary treats, or even dreaming about them.
For example, you might suddenly find yourself craving a candy bar after lunch, even though you weren't thinking about it before. Or you might feel an overwhelming desire for dessert immediately after dinner, even if you're already full. Afternoon energy dips can also become prime craving time, leading you to reach for sugary snacks for a quick boost.
While intense, these cravings are generally temporary. As your body adjusts to a lower sugar intake, the cravings will gradually decrease. This process allows you to become more aware of your true hunger cues and develop healthier eating habits. Learn more about Intense Sugar Cravings
However, these intense cravings can also present challenges. They can trigger episodes of binge eating, where you consume large quantities of sugary foods in an attempt to satisfy the craving. This can undermine your efforts to reduce sugar and lead to feelings of guilt and frustration. The constant battle against cravings can also cause decision fatigue, making it harder to make healthy food choices in other areas of your diet. Social situations involving food can become particularly difficult, as you may feel tempted to indulge in sugary treats offered by friends or family.
The infographic below visualizes the typical timeline of sugar cravings during withdrawal, highlighting the key milestones in this process.
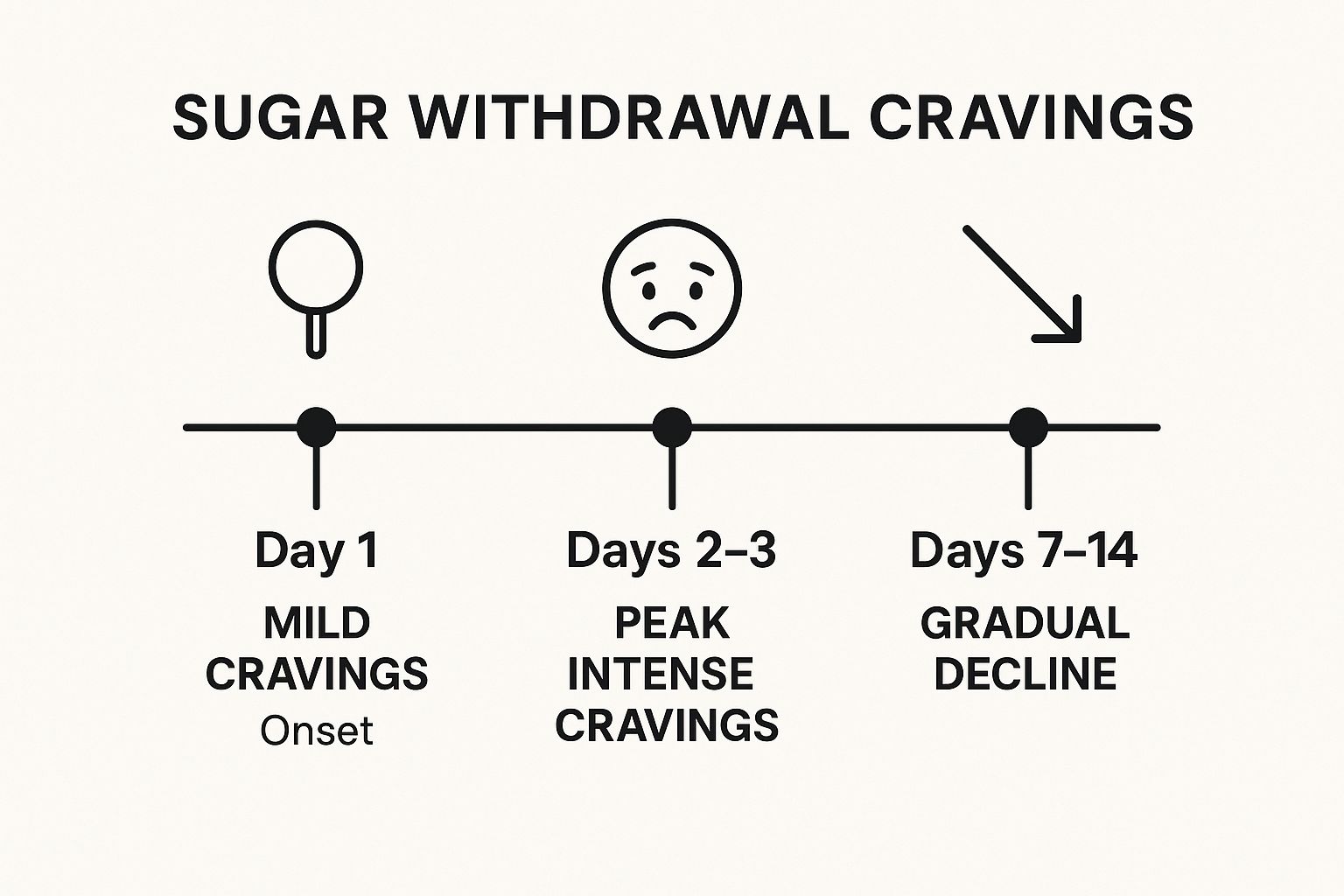
As the infographic illustrates, the first day typically marks the onset of mild cravings. These escalate to peak intensity around days 2-3, before gradually declining over the following week or two. Understanding this timeline can help you mentally prepare for the challenges ahead and stay committed to your goals.
To navigate these intense cravings, several strategies can be incredibly helpful. Eating protein-rich snacks can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce cravings. Staying hydrated is also essential, as dehydration can sometimes be mistaken for hunger or sugar cravings. Keeping healthy alternatives nearby, such as fruit or a handful of nuts, can provide a satisfying alternative when cravings hit. Practicing mindful breathing exercises can also help you manage the emotional and psychological aspects of cravings, allowing you to observe the craving without giving in to it.
Remember, overcoming sugar cravings is a challenging but achievable goal. By understanding the underlying mechanisms, anticipating the timeline of withdrawal symptoms, and implementing effective coping strategies, you can successfully navigate this initial phase and pave the way for a healthier, more balanced relationship with sugar.
2. Fatigue and Energy Crashes
One of the most common and frustrating sugar withdrawal symptoms is a profound sense of fatigue and energy crashes. This draining sensation occurs as your body adjusts to functioning without the constant influx of sugar it's become accustomed to. For many, sugar serves as a primary source of quick energy. Think of it like constantly topping off your gas tank with small amounts of fuel – you're always running, but never truly filled. When you cut off that sugar supply, your body essentially sputters, struggling to find an alternative energy source. It's like switching from a readily available but inefficient fuel to a more sustainable one – there's an adjustment period. This transition leads to a significant dip in energy levels, affecting both physical and mental performance until your metabolism adapts to burning fat and other fuel sources more effectively. This adaptation is a key step towards achieving stable, long-term energy levels. You are, in essence, retraining your body to utilize its own resources more efficiently. This is a crucial component of overcoming sugar addiction and experiencing lasting health benefits.

This fatigue is usually most intense during the first week of sugar withdrawal. While it impacts both physical and mental energy, many individuals find the afternoon slump particularly challenging. This is often when the effects of sugar withdrawal, combined with the natural circadian rhythm dip, create a perfect storm of exhaustion. This afternoon energy crash can manifest as not only physical tiredness but also mental fatigue, commonly referred to as "brain fog." This foggy feeling can make concentrating, problem-solving, and even simple decision-making feel like a monumental task.
While this fatigue is a hallmark of sugar withdrawal symptoms, it's crucial to understand it is temporary. This is a crucial point – the exhaustion isn't permanent. While navigating this period can be challenging, recognizing it as a transient phase can be incredibly motivating. In fact, pushing through this initial period of fatigue leads to more stable energy levels in the long run. Imagine a car finally switching to a reliable, high-octane fuel source – it runs smoother, longer, and with more consistent power. Similarly, your body, once adapted to burning fat efficiently, will experience fewer energy peaks and valleys, leading to sustained energy throughout the day. This sustained energy can positively influence other areas of your life, including sleep. By eliminating the sugar-induced energy spikes and crashes, you pave the way for more regulated sleep patterns and better sleep quality.
However, it’s important to acknowledge the downsides of this withdrawal symptom. Reduced energy can significantly impact work performance, making it harder to focus and complete tasks efficiently. It can also sap your motivation to exercise, which is ironically a great way to combat fatigue in the long run. Furthermore, this tiredness can make it challenging to fulfill daily responsibilities, from childcare to household chores. Think of everyday tasks feeling like climbing a hill while carrying a heavy backpack.
For example, you might find yourself completely drained by 2 PM, even without consuming your usual sugary afternoon snacks. You might also rely on multiple cups of coffee just to get through the workday, a habit that can further disrupt sleep and exacerbate the cycle of fatigue. Even your regular workout routine might feel impossible to complete, leaving you feeling frustrated and further depleted.
To combat these energy crashes and minimize their impact, there are several actionable strategies you can implement. Focus on consuming complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. These provide a slow and steady release of energy, preventing the dramatic spikes and crashes associated with simple sugars. If possible, take short power naps (20-30 minutes) during the day to recharge. Getting morning sunlight exposure can also help regulate your circadian rhythm and improve energy levels. Finally, consider incorporating B-vitamin rich foods into your diet, as these vitamins play a vital role in energy production. These strategies are not quick fixes but rather sustainable approaches to managing your energy levels during sugar withdrawal. They provide your body with the tools it needs to successfully transition to a more stable and efficient energy system.
3. Mood Swings and Irritability
One of the most challenging sugar withdrawal symptoms is the emotional rollercoaster of mood swings and increased irritability. This is a common experience as your body adjusts to functioning without the constant influx of sugar it's become accustomed to. Understanding the underlying causes and implementing coping strategies can significantly ease this transition and pave the way for a healthier, more balanced you. This symptom deserves a prominent place on the list of sugar withdrawal symptoms because it can significantly impact daily life, affecting relationships, work performance, and overall well-being.
Sugar plays a significant role in brain chemistry, particularly affecting the production and regulation of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, often referred to as the "feel-good" chemicals. When you consume sugar, these neurotransmitters are released, leading to a temporary sense of pleasure and well-being. However, this effect is short-lived, and as blood sugar levels drop, so do these neurotransmitter levels, leading to a crash. Over time, consistent high sugar intake creates a cycle of highs and lows, conditioning your brain to crave sugar for that temporary mood boost.
During sugar withdrawal, your body and brain are essentially recalibrating. As your blood sugar levels stabilize and neurotransmitter production adjusts to a sugar-free state, you may experience significant mood disruptions. These unpredictable emotional responses can manifest as:
- Unpredictable emotional responses: One moment you might feel fine, and the next, you could be inexplicably tearful or angry. This emotional volatility can be unsettling and make it difficult to navigate daily interactions.
- Increased sensitivity to stress: Everyday stressors that you normally handle with ease might feel overwhelming during sugar withdrawal. Your tolerance for frustration may decrease, leading to feelings of anxiety or being easily agitated.
- Anxiety or depression-like symptoms: While not clinically diagnosed anxiety or depression, you may experience symptoms that mimic these conditions, such as feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or excessive worry. This is a temporary side effect of the brain chemistry rebalancing and will subside as your body adapts.
- Correlation with meal timing: Mood swings and irritability can be particularly pronounced around meal times, especially if you were accustomed to sugary snacks or drinks between meals. This is because your body anticipates the usual sugar rush and reacts to its absence.
While navigating these emotional shifts can be difficult, it's important to remember that they are a sign of progress. These are the pros of experiencing this particular sugar withdrawal symptom:
- Indicates brain chemistry is rebalancing: The mood swings, while unpleasant, are evidence that your brain is breaking free from its dependence on sugar and returning to a more balanced state of neurotransmitter production.
- Leads to more emotional stability long-term: Once you’ve overcome the initial withdrawal phase, you’ll likely experience greater emotional stability and resilience. You'll be less susceptible to the dramatic highs and lows associated with sugar consumption.
- Increases self-awareness of food-mood connection: Going through sugar withdrawal can be a powerful learning experience. It highlights the profound impact that food choices have on your mood and overall well-being, empowering you to make more conscious decisions in the future.
However, there are downsides to consider:
- Can strain relationships: The irritability and unpredictable emotional responses can strain relationships with family, friends, and colleagues.
- May affect work performance: Difficulty concentrating and increased sensitivity to stress can negatively impact productivity and work performance.
- Can trigger emotional eating: The emotional discomfort of withdrawal can tempt you to return to sugar for comfort, perpetuating the cycle of dependence.
To navigate these challenges, consider the following tips:
- Practice stress management techniques: Engage in activities like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature to help manage stress and regulate your mood.
- Inform close contacts about your situation: Let your family and friends know that you’re going through sugar withdrawal and explain how it might affect your behavior. This can foster understanding and patience.
- Maintain regular meal times: Eating regular, balanced meals helps stabilize blood sugar levels, reducing the likelihood of mood swings.
- Consider magnesium supplementation: Magnesium plays a role in mood regulation and can be beneficial during withdrawal. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
Nutritionist Dawn Jackson Blatner and Dr. Mark Hyman, among others, have extensively researched and popularized the connection between food and mood. Their work emphasizes the importance of dietary changes, particularly reducing sugar intake, for improved mental and emotional well-being. Successfully navigating sugar withdrawal and overcoming mood swings and irritability is a testament to your commitment to a healthier lifestyle. It’s a crucial step towards achieving long-term emotional stability and a more balanced relationship with food.
4. Headaches
Headaches are a common sugar withdrawal symptom, often arising as your body adjusts to functioning without its usual influx of sugar. This unpleasant side effect, ranging from mild tension headaches to more severe migraines, is a direct result of the physiological changes happening within your brain and circulatory system. When you consume sugar regularly, your blood sugar levels experience dramatic peaks and valleys. Cutting off this sugar supply forces your body to adapt, leading to fluctuations in blood sugar and impacting brain chemistry. These shifts can trigger pain receptors and affect blood vessel dilation, resulting in the throbbing or aching sensation we recognize as a headache. This symptom underscores the profound impact sugar has on our system, making headaches a clear sign that your body is undergoing a significant detox process.
Headaches related to sugar withdrawal typically emerge within the first 24-48 hours after reducing sugar intake. They often manifest as a dull ache or a sharp, throbbing pain, frequently accompanied by neck tension. Many individuals report experiencing these headaches more intensely in the morning or late afternoon. For instance, you might wake up with throbbing temples during the first few days of cutting back on sugar, or experience tension headaches that worsen with the stress of the workday. Some individuals find that morning headaches improve after eating a balanced breakfast, as this helps stabilize blood sugar levels. Another example is experiencing a lingering dull ache throughout the day that intensifies towards the evening. These varied experiences highlight the individual nature of withdrawal symptoms.
While experiencing headaches during sugar withdrawal can be debilitating and interfere with daily activities, understanding their underlying cause and employing effective management techniques can significantly alleviate discomfort.
Pros of Experiencing Headaches During Sugar Withdrawal:
- Clear indicator of detox process: Headaches serve as a tangible sign that your body is actively adjusting to a reduced sugar intake and initiating the detoxification process.
- Usually resolve within a week: The good news is that these headaches are usually temporary and tend to subside within a week as your body adapts.
- Not dangerous, just uncomfortable: While undoubtedly unpleasant, sugar withdrawal headaches are not inherently dangerous, simply uncomfortable.
Cons of Experiencing Headaches During Sugar Withdrawal:
- Can be debilitating: The severity of headaches can range from mild to severe, potentially impacting your ability to function normally.
- May require pain medication: Some individuals may find over-the-counter pain relievers necessary to manage the discomfort.
- Can trigger other symptoms like nausea: In some cases, severe headaches can be accompanied by nausea, further compounding the discomfort.
Tips for Managing Sugar Withdrawal Headaches:
- Stay well-hydrated: Dehydration can exacerbate headaches, so ensure you’re drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Apply cold or warm compresses: Experiment with both cold and warm compresses on your forehead or neck to find what provides the most relief.
- Practice gentle neck stretches: Neck tension often accompanies these headaches, so gentle stretches can help alleviate the pain.
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule: Adequate and regular sleep is crucial for overall well-being and can help minimize headache frequency and intensity.
Understanding that headaches are a common and temporary sugar withdrawal symptom can empower you to navigate this challenging period. By recognizing the features, understanding the pros and cons, and implementing the provided tips, you can effectively manage these headaches and stay on track toward achieving your health goals. Remember, these headaches are a temporary hurdle on your path to a healthier, sugar-free lifestyle. This symptom deserves its place on the list of sugar withdrawal symptoms because it underscores the physiological impact of sugar on our bodies and reinforces the importance of addressing sugar dependence. While there is no specific website link to offer at this time, consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and support during your sugar withdrawal journey.
5. Sleep Disturbances
Sugar withdrawal can significantly impact your sleep, leading to a frustrating cycle of fatigue and cravings. This is a common sugar withdrawal symptom and understanding why it happens can empower you to address it effectively. Disrupted sleep patterns, including difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and experiencing restful sleep, are frequently reported during the initial stages of reducing sugar intake. This makes sleep disturbances a key symptom to be aware of when you're cutting back on sugar.
The connection between sugar and sleep is complex and involves several hormonal and metabolic processes. Consuming sugar, especially refined sugars, can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels. These fluctuations can cause a surge in energy followed by a crash, which disrupts the delicate balance required for healthy sleep. Moreover, sugar intake affects the production of cortisol, a stress hormone, and melatonin, the sleep hormone. Elevated cortisol levels interfere with melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep. The body's adjustment to a lower sugar intake can significantly impact circadian rhythms, the internal clock regulating sleep-wake cycles. This disruption can manifest in several ways.
Features of Sugar Withdrawal-Related Sleep Disturbances:
- Insomnia or restless sleep: You might find yourself tossing and turning, unable to quiet your mind and drift off to sleep.
- Waking up at 2-4 AM: This is a common occurrence during sugar withdrawal. Blood sugar fluctuations during the night can trigger wakefulness during these early morning hours.
- Vivid or disturbing dreams: Some individuals report experiencing more intense or unsettling dreams while going through sugar withdrawal.
- Morning grogginess despite adequate sleep time: Even if you manage to get a full eight hours of sleep, you might still wake up feeling tired and unrefreshed.
Examples:
- Lying awake thinking about food, particularly sugary treats, is a common experience during sugar withdrawal. This can be driven by cravings and the body's attempt to regain its usual sugar intake.
- Waking up multiple times per night, often accompanied by difficulty falling back asleep, further disrupts the sleep cycle and contributes to daytime fatigue.
- Feeling unrefreshed despite 8 hours of sleep highlights the impact of sugar withdrawal on sleep quality. Even if you're technically getting enough sleep, the disruptions caused by blood sugar fluctuations and hormonal imbalances prevent you from reaching deep, restorative sleep stages.
Pros and Cons of Navigating Sleep Disturbances during Sugar Withdrawal:
Pros:
- Temporary Adjustment Period: The good news is that these sleep disturbances are usually temporary. As your body adjusts to a lower sugar intake, your sleep patterns should gradually normalize.
- Leads to Better Sleep Quality Long-Term: Overcoming the initial hurdle of sleep disruptions during sugar withdrawal can pave the way for significantly improved sleep quality in the long run. Stabilized blood sugar levels and balanced hormone production contribute to more restful and restorative sleep.
- Encourages Better Sleep Hygiene Habits: Dealing with sleep disturbances during withdrawal often motivates people to adopt healthier sleep hygiene practices, which benefits overall health and well-being.
Cons:
- Compounds Fatigue Symptoms: Sleep disturbances can exacerbate the fatigue already associated with sugar withdrawal, making it more challenging to maintain energy levels throughout the day.
- Can Affect Next-Day Performance: Poor sleep can negatively impact cognitive function, concentration, and productivity, making it harder to perform at your best.
- May Worsen Mood Symptoms: Sleep deprivation can worsen irritability, anxiety, and other mood-related symptoms, making the withdrawal process feel more challenging.
Tips for Managing Sleep Disturbances:
- Avoid screens 2 hours before bed: The blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with melatonin production.
- Try chamomile tea or magnesium: Chamomile tea has calming properties that can promote relaxation and sleep. Magnesium is a mineral involved in regulating sleep.
- Keep bedroom cool and dark: A cool, dark environment is conducive to better sleep.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Deep breathing exercises, meditation, or gentle stretching can help calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep.
Renowned sleep specialist Dr. Matthew Walker has extensively discussed the detrimental impact of sugar on sleep quality, emphasizing the importance of addressing sugar intake for optimal sleep health. While navigating sleep disturbances during sugar withdrawal can be challenging, remember that this is a temporary phase. By implementing these tips and understanding the underlying mechanisms connecting sugar and sleep, you can overcome this hurdle and achieve long-term improvements in your sleep quality and overall well-being. This ultimately reinforces why addressing sleep disturbances is a vital part of successfully managing sugar withdrawal symptoms.
6. Difficulty Concentrating
Sugar withdrawal can manifest in various ways, and one of the more frustrating symptoms is difficulty concentrating. This cognitive impairment, often described as "brain fog," can significantly impact daily life, affecting everything from work productivity to simple conversations. Experiencing this symptom is a clear sign that your body is adjusting to functioning without its usual influx of sugar, but understanding why it happens and how to manage it can make the withdrawal process significantly easier. This symptom deserves a place on this list because it can be a surprising and sometimes debilitating side effect of reducing sugar intake, and knowing how to cope with it is crucial for successfully breaking free from sugar's hold.
So, why does cutting back on sugar lead to brain fog? It all boils down to how your brain uses energy. For many people on a high-sugar diet, glucose becomes the primary fuel source for the brain. When you drastically reduce sugar intake, your brain essentially experiences a fuel shortage. It hasn’t yet fully adapted to using alternative energy sources, such as ketones, efficiently. This transition period, while ultimately beneficial, can lead to a temporary dip in cognitive performance, affecting focus, memory, and mental clarity. This is a key aspect of understanding sugar withdrawal symptoms.
The features of this difficulty concentrating can vary but often include:
- Trouble completing tasks: Simple tasks that once felt effortless may now require significantly more effort and time. You might find yourself struggling to finish projects at work or even simple chores around the house.
- Forgetfulness: You might experience increased forgetfulness, such as misplacing items, forgetting appointments, or struggling to recall names or information. This can be particularly frustrating and impact both personal and professional life.
- Difficulty making decisions: Even minor decisions can feel overwhelming. Your ability to weigh options and come to a conclusion might be hampered, leading to indecisiveness and procrastination.
- Reduced productivity: The combined effects of impaired focus, forgetfulness, and difficulty making decisions can significantly reduce overall productivity at work, school, or even in managing household responsibilities.
While experiencing difficulty concentrating during sugar withdrawal can be challenging, it’s important to remember that it’s a temporary phase and a sign that your brain is adapting to better fuel sources.
Here are the pros and cons of experiencing this sugar withdrawal symptom:
Pros:
- Indicates brain is adapting to better fuel sources: The brain fog is a sign that your brain is learning to utilize ketones, a more efficient and sustainable fuel source than glucose. This metabolic shift can lead to improved long-term cognitive function and sustained energy levels.
- Usually improves within 2 weeks: For most people, the difficulty concentrating significantly improves within one to two weeks of reducing sugar intake, as the brain becomes more adept at using alternative fuel sources.
- Can lead to enhanced mental clarity long-term: Once past the initial withdrawal phase, many individuals report experiencing increased mental clarity, improved focus, and better memory function as a result of reducing their sugar consumption.
Cons:
- Can affect work or school performance: Brain fog can make it difficult to focus on tasks, impacting productivity and performance in academic or professional settings.
- May cause frustration and stress: The feeling of not being able to think clearly can be frustrating and contribute to stress levels, especially when combined with other withdrawal symptoms.
- Can compound other withdrawal symptoms: Difficulty concentrating can exacerbate other withdrawal symptoms, such as fatigue and irritability, making the overall withdrawal process feel more challenging.
Here are some examples of how difficulty concentrating might manifest:
- Forgetting common words during conversations: You might find yourself pausing mid-sentence, struggling to recall a simple word, or using incorrect words altogether.
- Reading the same paragraph multiple times: Comprehending written material might require more effort, leading to rereading the same text multiple times to grasp the meaning.
- Unable to focus during meetings or classes: Maintaining attention during meetings, lectures, or presentations can become challenging, making it difficult to absorb information and participate effectively.
To navigate this phase of sugar withdrawal, here are some actionable tips:
- Break tasks into smaller chunks: Instead of tackling large, overwhelming tasks, break them down into smaller, more manageable steps. This can make the process less daunting and provide a sense of accomplishment as you complete each step.
- Use memory aids and lists: Utilize tools like to-do lists, calendars, and reminders to help compensate for forgetfulness and stay organized.
- Take frequent breaks: Give your brain regular breaks throughout the day to avoid mental fatigue. Short periods of rest can help improve focus and concentration.
- Consume omega-3 rich foods: Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health and can support cognitive function. Include foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts in your diet.
By understanding the reason behind difficulty concentrating during sugar withdrawal and implementing these strategies, you can effectively manage this symptom and continue on your path to a healthier, sugar-free lifestyle.
Sugar Withdrawal Symptoms Comparison
| Symptom | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements 💡 | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intense Sugar Cravings | Moderate: peaks 2-3 days, lasts 1-2 weeks | Requires protein-rich snacks, hydration, alternatives | Reduced cravings over time, better food awareness | Early phase of sugar withdrawal, stress-triggered cravings | Indicates detox progress, decreases gradually |
| Fatigue and Energy Crashes | Moderate: most severe in first week | Complex carbs, naps, sunlight, B-vitamins | Stabilized energy in 1-2 weeks | Adjusting metabolism post sugar, managing physical/mental tiredness | Leads to stable energy long-term |
| Mood Swings and Irritability | Moderate-High: unpredictable emotions | Stress management, regular meals, magnesium | More emotional stability long-term | Managing emotional rebalancing during withdrawal | Increases self-awareness of mood-food links |
| Headaches | Low-Moderate: onset within 24-48 hours | Hydration, compresses, neck stretches, sleep | Usually resolve within 3-7 days | Early detox symptom, physical discomfort control | Clear detox indicator, non-dangerous |
| Sleep Disturbances | Moderate: disrupted sleep patterns | Screen avoidance, relaxation, cool environment | Improved sleep quality after adjustment | Addressing circadian rhythm disruption | Encourages better sleep hygiene |
| Difficulty Concentrating | Moderate: impaired focus and memory | Break tasks down, memory aids, omega-3 foods | Improved cognition within 7-14 days | Coping with brain fog and reduced productivity | Leads to enhanced long-term mental clarity |
Reclaiming Your Health: Life After Sugar
Navigating sugar withdrawal is a significant step toward reclaiming your health and well-being. This article has outlined some of the common sugar withdrawal symptoms you might experience, such as intense sugar cravings, fatigue and energy crashes, mood swings and irritability, headaches, sleep disturbances, and difficulty concentrating. Remember, these symptoms are temporary and a sign that your body is adjusting to a healthier state – a life with less reliance on sugar.
By understanding these sugar withdrawal symptoms and implementing practical strategies, you can minimize discomfort and emerge stronger on the other side. Mastering these concepts is valuable because it empowers you to break free from the cycle of sugar cravings and enjoy sustained energy levels, improved mood stability, better sleep, and enhanced cognitive function. This translates to a greater sense of overall well-being and reduces your risk of developing sugar-related health issues like obesity and diabetes.
You've got this! Ready to take control of your sugar intake and navigate withdrawal symptoms with ease? Download StopSugar today at StopSugar and access personalized support, tracking tools, and helpful resources designed to help you manage cravings and achieve your health goals.