Artificial Sweeteners vs Natural Sugar A Comprehensive Health Guide

The real heart of the artificial sweeteners vs. natural sugar debate comes down to this: natural sugars give you calories and spark a direct response from your metabolism. On the other hand, artificial sweeteners pack an intense sweet punch with few or no calories, but their interaction with our bodies is a lot more complex and indirect.
Figuring out which is "healthier" is impossible without context. It all comes down to your personal health goals.
Navigating the Sweetener Dilemma
The conversation around artificial sweeteners and natural sugar is usually oversimplified, painting one as "good" and the other as "bad." The truth is far more nuanced. The first step is to really understand their fundamental differences so you can make a conscious choice that actually fits your goals, not just trade one sweet for another.
The Shifting Landscape of Sweetness
Recent data shows a really interesting trend. Our global diet hasn't gotten any less sweet; we're just getting that sweetness from different places. Over the past decade, we've seen a huge shift away from traditional sugar and toward non-nutritive sweeteners (NNS).
Between 2007 and 2019, the amount of added sugar in beverages dropped by 12% worldwide. But at the same time, the use of NNS like aspartame and sucralose shot up by a massive 36%. For packaged foods, the total sweetness from both sugar and NNS actually climbed by nearly 8%. This tells us we’re just getting hooked on more intense sweetness overall. You can dig into the full study on global sweetener trends to see the data for yourself.
The core issue isn't just about choosing a sweetener; it's about addressing our collective reliance on intense sweetness. The goal is to reduce this dependency, not just substitute its source.
This guide is designed to move beyond those simplistic labels and give you a clear way to compare your options. We'll explore how each type of sweetener affects your body, from your metabolic health to your cravings. This knowledge is what empowers you to make truly informed choices—a journey where tools like the StopSugar app can provide invaluable support by helping you track habits and find healthier alternatives.
| Feature | Natural Sugar (e.g., Sucrose) | Artificial Sweeteners (e.g., Aspartame) |
|---|---|---|
| Caloric Content | Provides calories (approx. 4 per gram) | Zero or negligible calories |
| Metabolic Impact | Directly raises blood glucose and insulin | Generally does not directly raise blood sugar |
| Sweetness Intensity | Baseline standard for sweetness | 200 to 20,000 times sweeter than sugar |
| Primary Use Case | Energy source, browning in baking | Calorie reduction, sugar replacement |
Defining Natural Sugars and Artificial Sweeteners
Before we can really get into the nitty-gritty of artificial sweeteners versus natural sugar, we need to be clear on what each one actually is. They both deliver that sweet taste we crave, but that's where the similarities end. Their origins, how they're built chemically, and the way our bodies handle them are worlds apart.
At their core, natural sugars are simple carbohydrates found in nature. Think of them as the body's go-to source for a quick energy boost.
When you consume them, your body gets to work breaking them down into glucose. This signals your pancreas to release insulin, which acts like a key, unlocking your cells to let that energy in. It’s a beautifully efficient system, but problems arise when we overload it with too much sugar, too often.
A Closer Look at Natural Sugars
The natural sugars you run into most often are either single-molecule sugars (monosaccharides) or two of those molecules linked together (disaccharides).
- Sucrose: This is just your everyday table sugar. It’s a disaccharide, meaning it's one part glucose and one part fructose, usually pulled from sugar cane or sugar beets.
- Fructose: Known as "fruit sugar," this monosaccharide is what makes fruits, honey, and some root veggies taste sweet.
- Glucose: This is the big one—the body's main fuel. It's a monosaccharide found in foods like fruit and is the basic unit of most carbs.
Each of these sugars plays a slightly different role in your body. If you're curious to learn more, our guide on the difference between glucose and fructose is a great place to start. What they all have in common is that they provide energy, specifically about four calories per gram.
What Exactly Are Artificial Sweeteners?
On the flip side, we have artificial sweeteners. You’ll often hear these called non-nutritive sweeteners (NNS) because they’re designed to taste like sugar without the calories. Their chemical makeup is intentionally engineered to hit the sweet spot on your tongue, but they often do it with an intensity that blows regular sugar out of the water.
The real trick behind artificial sweeteners is that our bodies don't recognize them as a typical carbohydrate. Because of this, most of them pass right through our digestive system without being absorbed for energy, which is why they’re often labeled "zero-calorie."
This group is a mixed bag, containing everything from purely synthetic compounds to highly processed extracts from plants. When you see products like sugar-free syrups, they're using these compounds to deliver sweetness without the sugar load.
A few common ones you've probably heard of:
- Aspartame: Made from amino acids and packs a punch that's about 200 times sweeter than sugar.
- Sucralose: This is a chemically modified sugar molecule that's a whopping 600 times sweeter than the real thing.
- Stevia: This one comes from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, with extracts that can be up to 350 times sweeter than table sugar.
Comparing Sweetener Profiles at a Glance
To make things a bit clearer, it helps to see how these common sweeteners stack up against each other. This table gives you a quick snapshot of their source, calories, and just how sweet they really are compared to standard sugar.
| Sweetener Type | Examples | Source | Calories per Gram | Sweetness vs. Sugar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Sugars | Sucrose, Fructose, Glucose, Honey | Sugar cane, beets, fruits, honey | ~4 | 1x (baseline) |
| Artificial | Aspartame (Equal, NutraSweet) | Synthetic (amino acids) | 0 | ~200x |
| Artificial | Sucralose (Splenda) | Modified sugar molecule | 0 | ~600x |
| Plant-Derived | Stevia (Truvia, Pure Via) | Stevia rebaudiana plant | 0 | up to 350x |
| Sugar Alcohols | Erythritol, Xylitol | Fermented corn or plant fiber | ~0.2 - 2.6 | ~0.7x |
As you can see, the biggest difference lies in the intense sweetness and lack of calories in the artificial options. This mismatch—a powerful sweet signal without any energy to back it up—is at the heart of the debate and creates some unique effects on our bodies, which we'll dive into next.
How They Really Affect Your Body
Choosing between natural sugar and an artificial sweetener isn't just about taste. It's a decision that sends a cascade of different signals through your body, influencing everything from your energy levels to the trillions of tiny organisms living in your gut. Getting to the heart of the artificial sweeteners vs. natural sugar debate means understanding what happens after that first sweet bite.
This map gives a great overview of the two main sweetener categories, showing you exactly where common options fit in.
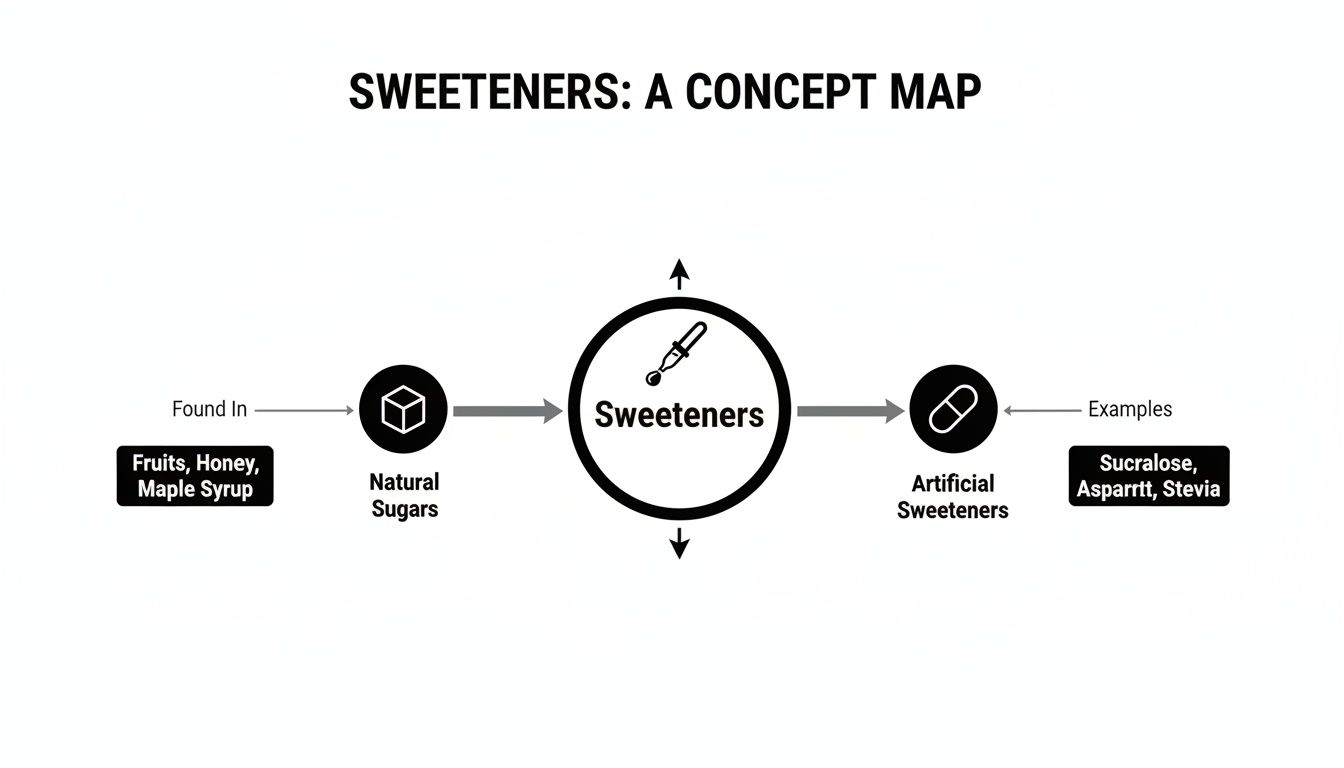
As you can see, even though they all deliver a sweet taste, their origins and chemical makeups are worlds apart. This is why your body handles them so differently.
Metabolic Health and Insulin Response
When you eat natural sugar, like the sucrose you stir into your coffee, your body knows exactly what to do. It breaks it down into glucose, which hits your bloodstream and raises your blood sugar. That's the cue for your pancreas to release insulin, the hormone that unlocks your cells so they can absorb that glucose for energy.
It’s a straightforward biological process: sugar gives you calories, and insulin helps you use or store them. The trouble is, a constant flood of sugar can wear out this system. Over time, your cells can become resistant to insulin's signals, a condition that’s a major stepping stone toward serious metabolic problems.
Artificial sweeteners throw a wrench in that process. Since they don't contain glucose and offer zero calories, they don't trigger that immediate insulin spike. This is why they're often marketed as a safe bet for managing blood sugar.
But the story isn't quite that simple. We're now learning that some artificial sweeteners might have a more indirect effect. Some studies suggest they can alter gut bacteria in a way that messes with how our bodies handle glucose later on. Others theorize that the intensely sweet taste alone might trick our bodies into expecting a sugar rush that never comes, potentially confusing our natural metabolic responses.
The Gut Microbiome Connection
Your gut is like a bustling city of trillions of microorganisms, all working to manage digestion, support your immune system, and even influence your mood. What you eat is the food source for this entire ecosystem, and sugars and sweeteners are two very different meals.
Natural sugars are a quick and easy feast for many gut microbes. A diet high in simple sugars can encourage certain types of bacteria and yeast to overgrow, throwing the delicate balance of your microbiome out of whack. This kind of imbalance can lead to inflammation and digestive trouble.
Artificial sweeteners are a different story entirely. Many of them, like sucralose and saccharin, can't be digested by our bodies. They travel all the way down to the colon, where they come into direct contact with our gut bacteria.
Studies have shown that some artificial sweeteners can alter the composition and function of the gut microbiome. By changing the types of bacteria that thrive, they may impact everything from nutrient absorption to metabolic regulation.
This interaction is a huge area of ongoing research because we're realizing just how deeply our gut health is tied to our overall well-being. So, your choice of sweetener directly impacts the kind of environment you're creating for these vital microbes.
Brain Chemistry, Cravings, and Mood
Maybe the most powerful effect of any sweetener happens in the brain. Sweetness—whether from sugar or a substitute—activates the dopamine pathways in our brain's reward center. It feels good, and our brain tells us to do it again.
The issue with many sweeteners is their sheer intensity. While they might cut calories, they can keep your brain hooked on an extreme level of sweetness, which is a major hurdle if you're trying to beat cravings. Many common artificial sweeteners are 200–600 times sweeter than table sugar. Even "natural" options like stevia (200–350 times sweeter) and monk fruit (100–250 times sweeter) pack an incredible punch.
This hyper-sweetness essentially trains your taste buds and brain to expect that level of intensity all the time. As clinicians often point out, people who regularly use these sweeteners can find naturally sweet foods, like fresh fruit, totally unsatisfying. You can dig deeper into how sweeteners impact cravings and the brain.
This "sweetness overload" creates a vicious cycle where your palate gets dulled, and you start needing more intense flavors to feel satisfied. For anyone using an app like StopSugar, recognizing this cycle is the first step to breaking free. The app’s daily check-ins are perfect for helping you connect the dots between your mood swings or energy crashes and your intake of intensely sweet foods—whether they have calories or not.
Weighing the Long-Term Health Risks
When you're trying to choose between artificial sweeteners and natural sugar, the conversation almost always lands on long-term health. We all want to know what's best for managing weight and avoiding chronic disease. The risks of eating too much sugar are pretty clear-cut, but the story with artificial sweeteners is a lot murkier.
It's no secret that a diet high in natural sugar can pack on the pounds. Sugar is dense with calories, and when you consume more energy than you burn, your body stores the excess as fat. This is a direct line to weight gain and obesity, which opens the door to a whole host of metabolic problems.
Over the years, all that extra sugar can trigger chronic inflammation, mess with your insulin response, and seriously increase your risk for type 2 diabetes and heart disease. The scientific evidence on this is solid and accepted by health experts all over the world.
The Artificial Sweetener Paradox
This is where artificial sweeteners entered the picture. They were created to give us that sweet taste without the calories, which sounds like the perfect fix for weight control, right? In the short run, that often holds true. Some studies show that swapping sugar for a non-nutritive sweetener can help you cut back on calories and even lose a little weight.
But when you zoom out and look at the long-term picture, the debate gets heated. Major health organizations are starting to pump the brakes on recommending them for sustained weight management. This creates a confusing paradox: if they have no calories, why are they linked to potential health issues down the road?
Unpacking the WHO's Long-Term View
A huge systematic review by the World Health Organization (WHO) really shines a light on this complexity. After digging through over 280 studies on sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose, they found two very different stories.
In short, controlled trials, yes, people did cut their daily intake by about 136 kcal and ate less sugar. But when researchers followed people for many years, the results were jarring. Higher sweetener consumption was linked to a 76% higher risk of obesity and a 23% higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
Now, the WHO was careful to label this long-term evidence as "low" certainty. That means it's not definitive proof that sweeteners cause these problems, but it's a big enough red flag to be cautious. Because of this, the WHO now officially recommends against using non-sugar sweeteners for long-term weight control. You can dig into the WHO's guidance on non-sugar sweeteners to get the full picture.
The bottom line? While sweeteners might help you cut calories for a little while, they probably aren't the magic bullet for preventing chronic disease over the course of your life.
Interpreting the Risks
So, how do we make sense of this for our own choices? It’s crucial to remember that association isn't the same as causation. The data doesn't prove sweeteners are the direct cause of these health problems. It's entirely possible that people who are already at a higher risk for obesity and diabetes are the ones reaching for these products to begin with.
Still, researchers have some interesting theories. One idea is that the intense sweetness without any calories might scramble our body's natural ability to regulate hunger and energy. Another points to how sweeteners might alter our gut microbiome, which could throw our metabolic health out of whack over time. For a deeper dive, our article on the specific health risks of artificial sweeteners gets into the science behind these ideas.
Ultimately, the evidence suggests that just trading one intensely sweet thing for another might be missing the point. A more reliable path to good health is to reduce your overall reliance on that hyper-sweet taste and build your diet around whole, nutrient-dense foods. That's exactly the philosophy behind tools like the StopSugar app, which is designed to help you build lasting habits, not just find quick fixes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goals
The endless "artificial sweeteners vs. natural sugar" debate rarely lands on a clear winner. Truthfully, the "best" option isn't universal—it comes down to you, your immediate goals, and your long-term vision for your health. So, instead of a one-size-fits-all answer, let's explore how to make smarter choices based on real-life situations.
The most effective strategy isn't just about finding the perfect swap. It's about gradually reducing your overall reliance on intense sweetness. Sure, switching from a sugary soda to a diet one cuts calories, but both can keep that craving for hyper-sweet tastes alive and well.
Contextual Choices for Daily Situations
Your decision-making process should be flexible. What makes sense for your morning coffee probably isn't the right call when you're baking a birthday cake for your kid.
- For the Soda Drinker: If you’re trying to kick a daily soda habit, a diet soda can be a handy temporary bridge. It helps you break the cycle of sugar spikes and extra calories. But the long-term goal should be to move away from all intensely sweet drinks and toward things like water or unsweetened iced tea.
- For the Home Baker: When it comes to baking, sugar does more than just sweeten—it affects browning, texture, and moisture. Instead of swapping a cup of sugar for an artificial sweetener that might not perform well in the oven, you could just reduce the sugar in the original recipe. Another great option is using a smaller amount of a natural sugar like maple syrup, which brings its own delicious flavor.
- For the Coffee Aficionado: That daily coffee is a huge habit-forming moment. This makes it the perfect opportunity to retrain your palate. Instead of reaching for any sweetener, try adding a dash of cinnamon, a drop of vanilla extract, or some unsweetened almond milk for a little extra flavor.
The most effective approach is to make conscious choices that gradually lower your "sweetness set point." This means helping your taste buds adapt to and appreciate less intense flavors, making naturally sweet foods like fruit more satisfying.
Developing a Sustainable Strategy
Getting to the root of why you're reaching for something sweet is a game-changer. Are you stressed? Tired? Or is it just a habit? Once you understand the trigger, you can find a better solution than a simple swap.
This is where a tool like the StopSugar app can really shine. It’s like having a personal coach in your pocket, guiding you through these daily decisions. The daily check-ins help you connect your mood and energy levels with your sweetener choices, and the alternatives feature offers instant, healthier ideas when a craving hits. By focusing on the underlying habits, you can build a truly sustainable, less-sweet life.
Ultimately, the best choice is always the one that moves you closer to your health goals without creating a new dependency. For more ideas on how to navigate this, check out our guide on the best sugar substitutes and how to use them effectively.
How StopSugar Helps You Break the Sweetness Cycle
Knowing the difference between artificial sweeteners and natural sugar is one thing, but actually changing your habits is a whole different ballgame. The real goal is to break free from that constant need for intense sweetness, and that's where an app like StopSugar can be a game-changer. It's designed to give you the practical tools you need to turn information into action.
So many of us don't connect the dots between what we eat and how we feel. One of StopSugar’s most valuable features is the daily check-in and mood tracker. It’s a simple concept, but it helps you see the direct link between that diet soda at lunch and the energy slump you feel at 3 p.m. When you start seeing those patterns for yourself, making a different choice next time becomes much easier.
Immediate Support When Cravings Hit
Let's be honest, cravings are the biggest roadblock for most people. They can hit hard and fast, completely derailing your good intentions. That’s exactly why StopSugar built in a Panic Button.
Instead of white-knuckling it through a craving, the Panic Button gives you something constructive to do right now. It walks you through guided exercises, sends motivational nudges, or offers a quick distraction to get you over the hump. Think of it as having a supportive friend in your pocket. This approach works well alongside other strategies, and you can find helpful tips for managing specific food cravings that offer even more backup.
The key to long-term success isn't just resisting temptation; it's about having a proactive plan for when temptation inevitably strikes. StopSugar provides that plan, helping you build resilience one craving at a time.
Smart Swaps and Future Guidance
Just telling yourself "no" all the time rarely works in the long run. A better, more sustainable way is to find genuinely satisfying alternatives that don't depend on that hyper-sweet taste. StopSugar’s alternatives feature gives you practical swaps for common foods and drinks right when you need them. Craving a sweet coffee? Need a better afternoon snack? The app has ideas ready to go, helping you gradually retrain your taste buds.
And it's only getting smarter. StopSugar is developing an AI Coach that will offer support tailored specifically to you. This future feature will look at your check-ins, moods, and the times you struggle most to give you truly personal advice.
- Personalized Insights: The AI Coach will learn your unique triggers—like stress or boredom—and suggest ways to handle them.
- Proactive Nudges: It will send timely reminders and encouragement based on your own progress and patterns.
- Meal and Snack Ideas: The coach will suggest recipes and food choices that fit your goal of reducing overall sweetness.
By putting these tools together, StopSugar helps you move past the "artificial sweeteners vs. natural sugar" debate. It gives you what you need to build healthier, lasting habits and finally get off the sweetness rollercoaster for good.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to swapping sugar for sweeteners, a lot of questions pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones with practical, straightforward answers you can actually use.
Are Natural Sweeteners Like Stevia Really Better Than Aspartame?
It's easy to see "plant-derived" and think "healthier," but the reality is a bit more complicated. High-intensity sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit are heavily processed, just like synthetic ones like aspartame. In the end, they all do the same thing: deliver a massive hit of sweetness with zero calories.
The real issue isn't where they come from, but what they do to your taste buds. They keep you hooked on that intensely sweet flavor, which can make a naturally sweet piece of fruit taste bland. The goal shouldn't be to find the "best" fake sugar, but to slowly reduce your need for any kind of intense sweetness.
Will I Stop Craving Sugar if I Switch to Artificial Sweeteners?
Probably not. In fact, it can sometimes make things worse. While a diet soda might hit the spot in the moment, it doesn't solve the underlying craving. Because these sweeteners are often hundreds of times sweeter than actual sugar, they keep your brain's reward pathways firing on all cylinders, expecting that super-sweet taste.
This can lead to a rebound effect, making you crave other sweet or high-calorie foods later. A better strategy—and something the StopSugar app is designed for—is to gently dial down your overall sweetness intake. This gives your palate a chance to reset, and you'll find your cravings naturally start to fade.
The most sustainable way to beat cravings isn't finding a perfect substitute. It's retraining your taste buds to enjoy things that are less sweet, which makes whole foods taste amazing again.
What’s the Best Way to Sweeten My Coffee Without Sugar or Sweeteners?
The best long-term solution is to gradually reduce what you add until you can enjoy your coffee or tea black. But if you're not there yet, try adding flavor instead of just sweetness. This helps break the cycle.
Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- A little unsweetened almond or oat milk for a creamy texture.
- A shake of cinnamon or nutmeg for a warm, spicy flavor.
- Just one drop of pure vanilla extract for a rich, comforting aroma.
These additions make your drink more interesting without feeding a dependency on sugar. If you need more ideas for everyday food and drinks, the StopSugar app has a whole library of simple swaps to help you make better choices.